Dental & Facial Space Infection Treatment
in Naranpura, Ahmedabad
Expert Routine & Emergency Maxillofacial Care at Sanghvi Face & Dental Hospital
A dental infection that spreads beyond the tooth can quickly become a serious health risk. Known as a Facial Space Infection, these conditions require specialized knowledge of head and neck anatomy to treat effectively.
At Sanghvi Face & Dental Hospital, led by Dr. Darshan Sanghvi (MDS), we offer comprehensive protocols ranging from routine abscess management to emergency life-saving surgical interventions.
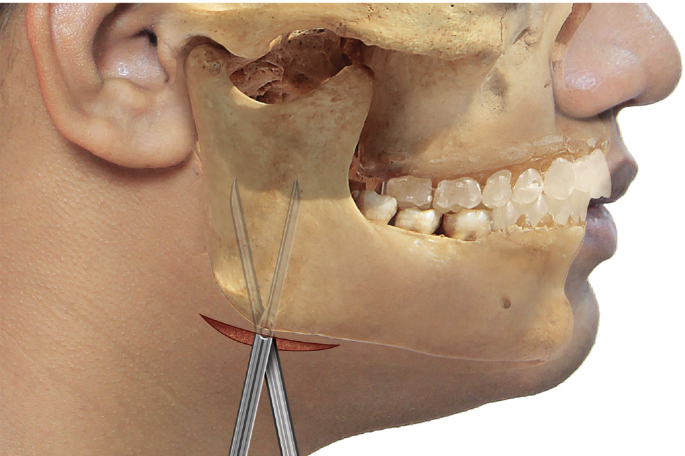
What is a Facial Space Infection?
A facial space infection refers to the spread of infection into the potential spaces between the facial and neck muscles. These spaces include areas like the buccal (cheek), submandibular (under the jaw), sublingual (under the tongue), masticator, temporal, and parapharyngeal spaces. These infections can rapidly expand, leading to swelling, restricted mouth opening, breathing difficulty, and even sepsis.
- Routine Treatment Protocols: Preventing the Spread
Most facial infections begin as a simple toothache. Our routine protocols are designed to stop the infection before it requires major surgery.
- Diagnostic Imaging: We use high-definition digital X-rays to locate the “offending tooth” and determine the extent of bone involvement.
- Abscess Management: For localized gum boils or dental abscesses, we perform minor drainage and deep cleaning of the infected site.
- Endodontic Intervention: If the tooth can be saved, Dr. Pallavi Sanghvi performs precision Root Canal Treatment (RCT) to remove the necrotic pulp—the source of the bacteria.
- Source Extraction: If a tooth is non-restorable, we perform a controlled extraction to prevent the bacteria from migrating into the deeper facial spaces.
- Emergency Protocols: Managing Severe Facial Swelling
When an infection enters the “fascial spaces” (the pathways between muscles), it becomes an emergency. Our hospital is equipped to handle these critical cases in Naranpura.
The Surgical Emergency Checklist:
If you experience difficulty breathing, inability to swallow, or swelling that is closing your eye, we initiate our emergency protocol:
- Airway Management: The highest priority is ensuring the swelling is not compressing the windpipe (airway).
- Incision & Drainage (I&D): Dr. Darshan Sanghvi performs a surgical incision—either intra-orally or extra-orally—to physically remove the pus and relieve the dangerous pressure within the facial compartments.
- Intravenous (IV) Antibiotics: Emergency cases often require high-dose antibiotics delivered directly into the bloodstream to bypass the digestive system and fight the infection immediately.
- Hospital-Grade Monitoring: We monitor the patient’s vitals to ensure the infection has not reached the bloodstream (Sepsis).
Understanding the “Spaces”: Where Infections Spread
Facial infections are classified by the anatomical “space” they occupy. Understanding these helps in precise surgical planning:
- Submandibular Space: Swelling under the jaw, often caused by lower molars.
- Buccal Space: Swelling in the cheek, typically from upper or lower premolars/molars.
- Canine Space: Swelling beside the nose, often originating from an infected eye tooth (canine).
- Ludwig’s Angina: A life-threatening, firm swelling under the tongue that pushes the tongue upward and backward, threatening the airway.
Causes of Facial Space Infection
Dental Infections
Untreated dental infections, especially infected molars, can lead to facial space infections.
Periapical Abscesses
Periapical abscesses, which are collections of pus at the root of a tooth, can spread to facial spaces.
Post-Extraction Infections
Infections that occur after a tooth extraction can spread to the surrounding facial spaces.
Trauma or Fractures
Trauma or fractures of the jaw or face can create pathways for infection to spread.
Salivary Gland Infections
Infections of the salivary glands can spread to the facial spaces.
Spread of Skin Infections
Skin or soft tissue infections can spread to the deeper facial spaces.
Symptoms of Facial Space Infection
- Swelling of the face, jaw, or neck
- Severe pain in the jaw or mouth
- Restricted mouth opening (trismus)
- Fever and chills
- Redness and warmth over the swollen area
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Difficulty breathing (airway compromise, in severe cases)
- Bad taste or pus drainage in the mouth
Why choose us
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Tailored to your unique needs and goals.
- Advanced Technology: Utilizing the latest dental and facial aesthetic innovations.
- Experienced Professionals: Our team of skilled dentists and surgeons are dedicated to excellence.
FAQs(Facial Space Infection )
Look for “red flag” symptoms: a firm swelling that is hot to the touch, difficulty opening your mouth (trismus), or a fever. If the swelling is visible on the outside of your face, it is no longer a simple toothache.
No. While painkillers mask the pain, they do not kill the bacteria. Antibiotics alone often cannot reach the center of an abscess. Physical drainage by a Maxillofacial Surgeon is the only definitive cure for a space infection.
Yes. For routine cases, local anesthesia is used. For complex emergency drainage, we offer sedation to ensure the patient remains comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
Contact the Naranpura Emergency Dental Team
- Specialist: Dr. Darshan Sanghvi (Con. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon & Implantologist)
- Location: Sanghvi Face and Dental Hospital, Opp Ankur Bus Stop, Naranpura, Ahmedabad , Gujarat – 13
- Contact: 079 – 27439850, 07990550920, 9824099850
- Book Your Appointment : https://calendar.app.google/ibP7s8QtjL6toUSRA
- Specialty: Routine Abscess Treatment | Emergency Incision & Drainage | Ludwig’s Angina Management

